Proper attic ventilation and adequate insulation is essential for maintaining a healthy and energy-efficient home.
It can save you thousands on utility bills and help to prevent issues like mold from costing you thousands more in repairs.
It helps regulate temperature, prevent moisture buildup, and extend the lifespan of your roof.
Proper attic ventilation can vary depending on your climate, roof design, and other factors. It’s essential to tailor your approach to the specific needs of your home.
Get a No-Cost Home Energy Assessment from NYSERDA today!
Here’s a guide on how to ventilate an attic properly:
- Assess Your Attic:
- Determine the current ventilation situation in your attic. Check for existing vents and their condition.
- Measure the square footage of your attic space to calculate the required ventilation.
- Calculate Ventilation Needs:
- The general guideline is to have at least 1 square foot of ventilation for every 150 square feet of attic space. This should be evenly divided between intake and exhaust ventilation.
- Types of Ventilation:
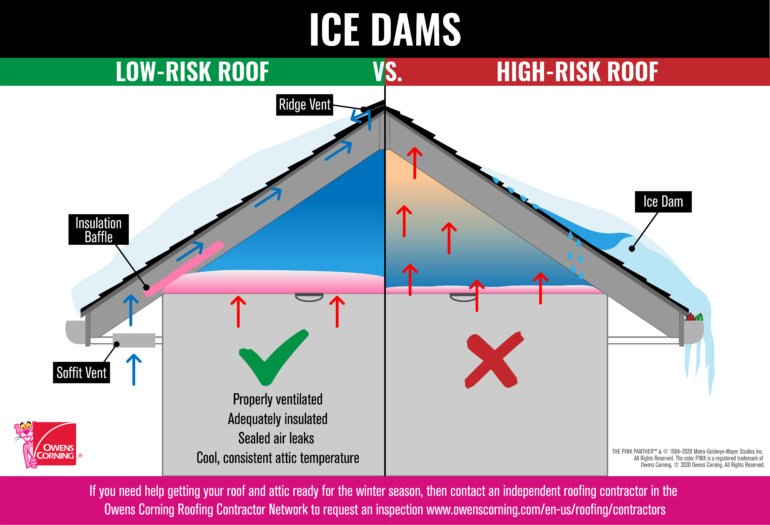
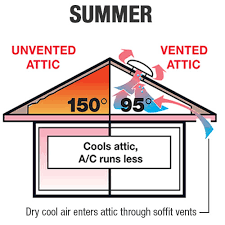
- Intake Ventilation: This is typically located along the eaves or soffits. It allows cool, outside air to enter the attic.
- Exhaust Ventilation: Placed near the roof’s peak, it allows warm, moist air to exit the attic.
- Ensure Proper Airflow:
- Use Natural Ventilation:
- Passive ventilation, such as ridge vents and soffit vents, can provide effective airflow without the need for mechanical systems.
- Install a ridge vent along the peak of the roof, combined with soffit vents for intake.
- Consider Mechanical Ventilation:
- If natural ventilation is insufficient, consider adding mechanical ventilation, such as attic fans.
- Solar-powered attic fans are energy-efficient and can help remove excess heat.
- Seal Air Leaks:
- Before installing ventilation, seal any gaps or cracks in the attic to prevent unwanted air exchange between the living space and the attic.
- Follow Local Building Codes:
- Be aware of local building codes and regulations regarding attic ventilation. They may specify the type and amount of ventilation required.
- Professional Assessment:
- If you’re unsure about the best approach, consult with a professional roofing or HVAC contractor. They can assess your specific situation and recommend the most effective ventilation solution.
NYS Licensed Home Inspector and Mold Assessor Kevin Michaels, Hudson Valley Property Inspections, LLC